1. 问题分析
我们在上一节爬取了网页的全部信息,下面我们还要这样html代码中找到我们所需要的内容,因此我们要根据问题进入网站中,去解析网页中的信息。
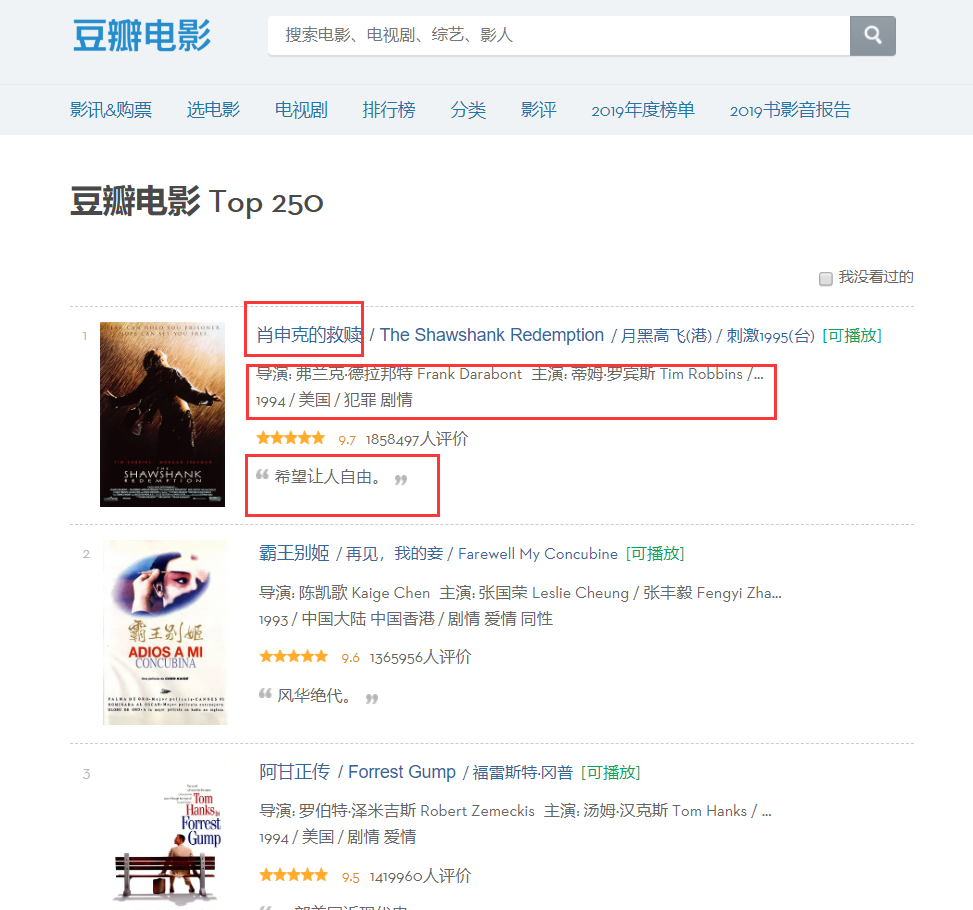
从页面中可以发现,我们需要爬取的信息分别存在于不同的分区当中,那么我们来检查一下页面的元素,右键页面检查网页源代码或者F12。
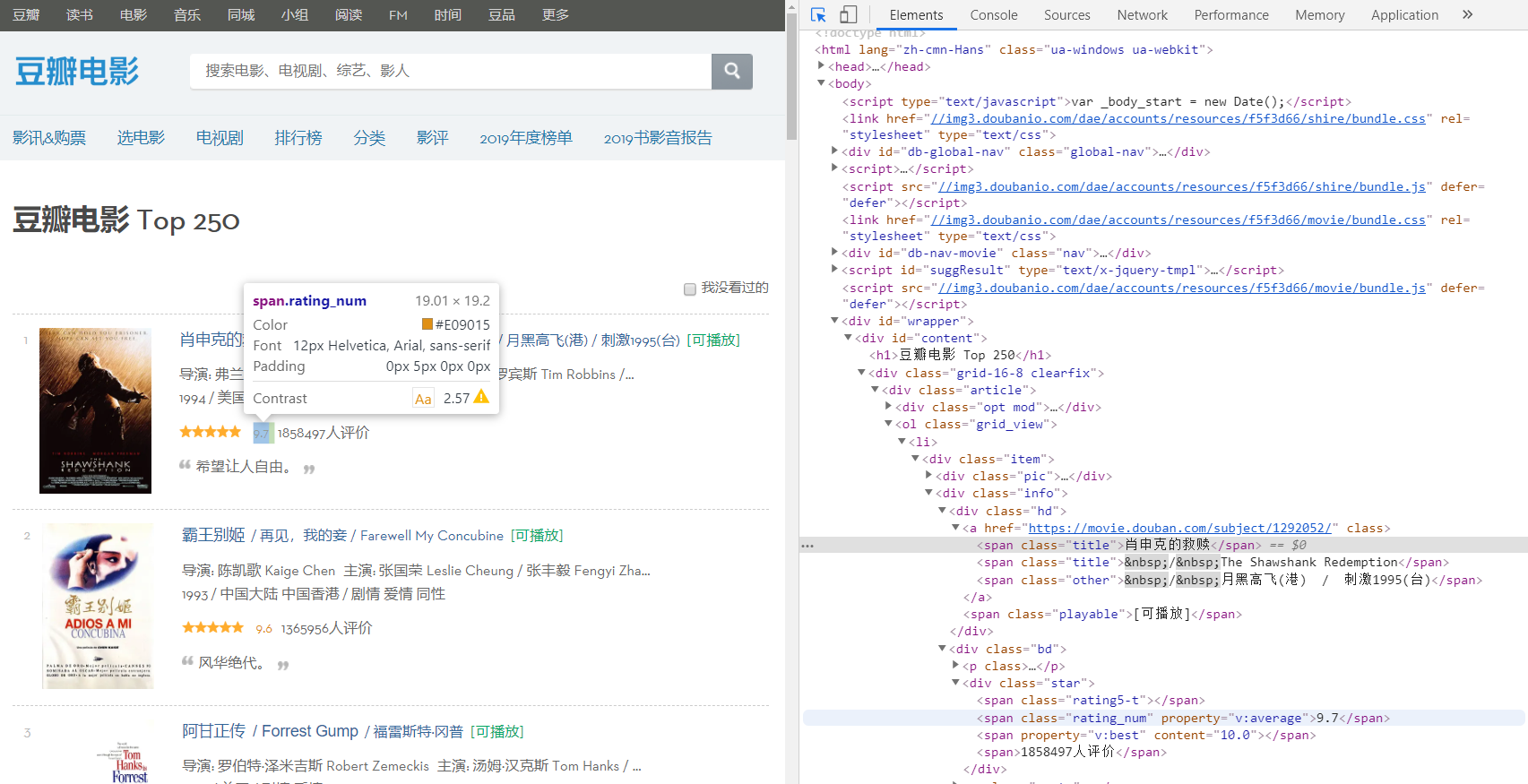
在分析网页之前,我们先规定一下解析之后的存储方式,这里我们采用列表来存储所有的信息,然后列表中的每一项对应一个字典,每一个字典再对应多种信息。
1 | movies = []#首先定义一个列表来存储所有信息 |
通过分析我们可以确定title的位置是名为‘hd’的‘div’下的第一个‘a’中的第一个‘span’,因此我们可以通过下面代码来锁定每一个电影的名字,然后放到一个字典中。
1 2 | moviename = each.find('div', class_='hd').a.span.text.strip()movie['title'] = moviename#字典的一项 |
相同的方式可以再根据定位找到导演名的源码,但是这个源码中包含了很多信息,所以我们要通过正则表达式进行过滤。
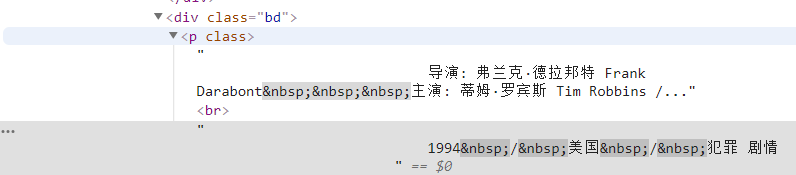
1 | info = each.find('div', class_='bd').p.text.strip() |
首先找到了这个标签下的所有内容,我们再通过正则表达式过滤掉无关信息。
1 2 3 4 5 | info = info.replace('\n', "")#过滤回车info = info.replace(" ", "")#过滤空格info = info.replace("\xa0", "")#过滤不间断空白符director = re.findall(r'[导演:].+[主演:]', info)[0]director = director[3:len(director) - 6] |
然后定义为字典的一项。
1 | movie['director'] = director#字典的一项 |
我们可以发现电影类型也在这个‘p’标签中,我们也直接通过正则表达式来获取该信息。
1 2 3 4 5 | plot = re.findall(r'[0-9]*[/].+[/].+', info)[0]plot = plot[1:]plot = plot[plot.index('/') + 1:]plot = plot[plot.index('/') + 1:]movie['plot'] = plot#添加为字典的 一项 |
最后再锁定评分信息。
1 2 | star = each.find('div', class_='star')star = star.find('span', class_='rating_num').text.strip() |
然后继续以字典的形式保存。
1 | movie['star'] = star |
最后把这个字典添加到列表中并遍历输出。
1 2 3 | movies.append(movie)#把字典加到列表中for i in movies:#遍历输出 print(i) |
2. 完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | import reimport requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupfor i in range(1): headers = {#模拟浏览器进行访问 'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/52.0.2743.82 Safari/537.36', 'Host': 'movie.douban.com' } res = 'https://movie.douban.com/top250?start='+str(25*i)#25次 r = requests.get(res, headers=headers, timeout=10)#设置超时时间 soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")#设置解析方式,也可以使用其他方式。 div_list = soup.find_all('div', class_='item') movies = [] for each in div_list: movie = {} moviename = each.find('div', class_='hd').a.span.text.strip() movie['title'] = moviename rank = each.find('div', class_='pic').em.text.strip() movie['rank'] = rank info = each.find('div', class_='bd').p.text.strip() info = info.replace('\n', "") info = info.replace(" ", "") info = info.replace("\xa0", "") director = re.findall(r'[导演:].+[主演:]', info)[0] director = director[3:len(director) - 6] movie['director'] = director release_date = re.findall(r'[0-9]{4}', info)[0] movie['release_date'] = release_date plot = re.findall(r'[0-9]*[/].+[/].+', info)[0] plot = plot[1:] plot = plot[plot.index('/') + 1:] plot = plot[plot.index('/') + 1:] movie['plot'] = plot star = each.find('div', class_='star') star = star.find('span', class_='rating_num').text.strip() movie['star'] = star movies.append(movie) for i in movies: print(i) |
3. 运行结果
控制台:

4. 总结
在这个实例中,我们主要学习如何去网页的源码中找到相应的信息,BeautifulSoup可以帮助我们迅速定位,再结合正则表达式来完成信息的匹配,下一节我们把这些数据保存到数据库当中。
C语言网提供由在职研发工程师或ACM蓝桥杯竞赛优秀选手录制的视频教程,并配有习题和答疑,点击了解:
一点编程也不会写的:零基础C语言学练课程
解决困扰你多年的C语言疑难杂症特性的C语言进阶课程
从零到写出一个爬虫的Python编程课程
只会语法写不出代码?手把手带你写100个编程真题的编程百练课程
信息学奥赛或C++选手的 必学C++课程
蓝桥杯ACM、信息学奥赛的必学课程:算法竞赛课入门课程
手把手讲解近五年真题的蓝桥杯辅导课程