一、项目介绍
这是一个用C语言输出的艺术字“HelloWorld!”。
还记得你第一次用C语言输出“HelloWorld!”吗?很简单吧!
编译环境:VC6
第三方库:Easyx2022 注意需要提前安装easyX,如没有基础可以先了解easyX图形编程
二、运行截图
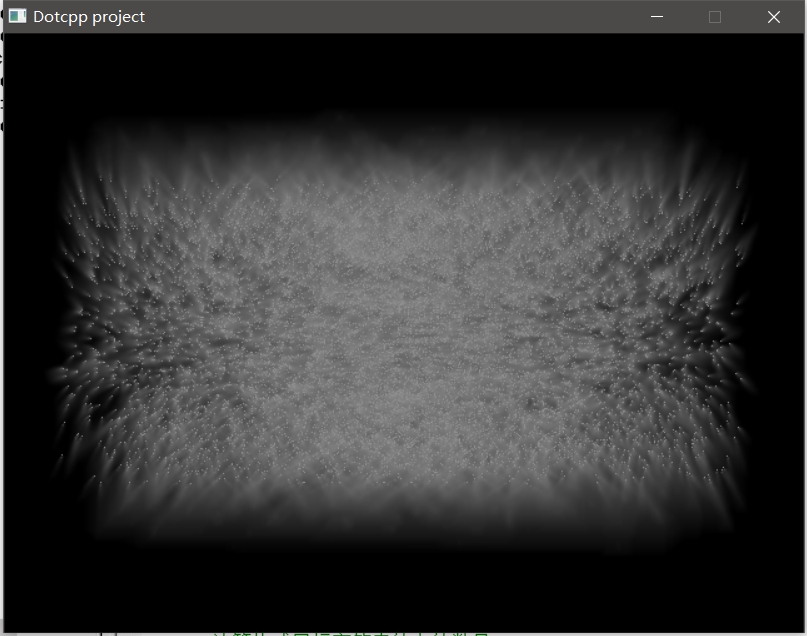
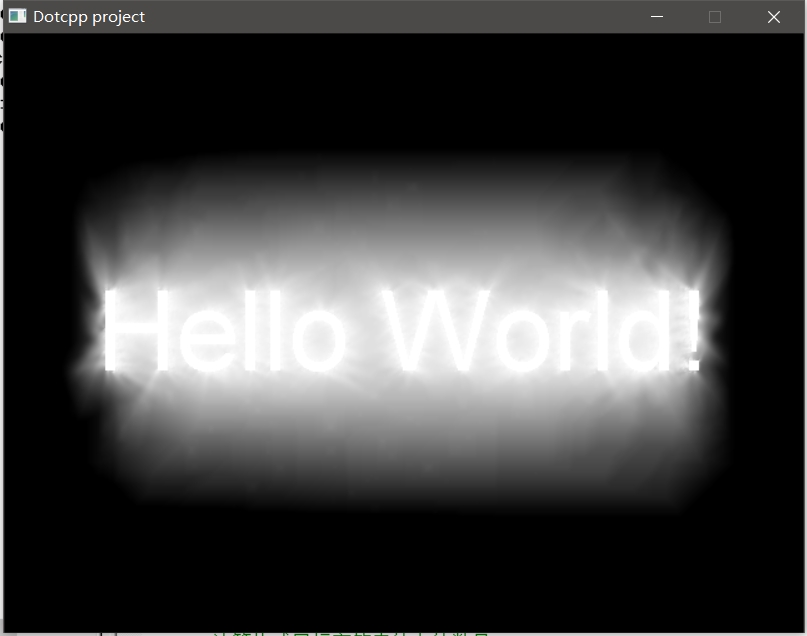
三、代码思路
1.引入图形库头文件
1 | #include <graphics.h> |
2.定义全局变量
1 2 3 4 5 | POINT *g_pDst;POINT *g_pSrc;int g_nWidth;int g_nHeight;int g_nCount; |
3.主函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | void main(){initgraph(640, 480);DWORD* pBuf = GetImageBuffer();GetDstPoints();GetSrcPoints();int x, y;for (int i = 2; i <= 256; i += 2){COLORREF c = RGB(i - 1, i - 1, i - 1);Blur(pBuf);for (int d = 0; d < g_nCount; d++){x = g_pSrc[d].x + (g_pDst[d].x - g_pSrc[d].x) * i / 256;y = g_pSrc[d].y + (g_pDst[d].y - g_pSrc[d].y) * i / 256;pBuf[y * 640 + x] = c;}Sleep(5);} |
四、完整源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 | #include <graphics.h>#include <conio.h>#include <time.h>// 定义全局变量POINT *g_pDst;// 点集(目标)POINT *g_pSrc;// 点集(源)int g_nWidth;// 文字的宽度int g_nHeight;// 文字的高度int g_nCount;// 点集包含的点的数量// 获取目标点集void GetDstPoints(){// 设置临时绘图对象IMAGE img;SetWorkingImage(&img);// 定义目标字符串TCHAR s[] = _T("Hello World!");// 计算目标字符串的宽高,并调整临时绘图对象的尺寸setcolor(WHITE);setfont(100, 0, _T("Arial"));g_nWidth = textwidth(s);g_nHeight = textheight(s);Resize(&img, g_nWidth, g_nHeight);// 输出目标字符串至 img 对象outtextxy(0, 0, s);// 计算构成目标字符串的点的数量int x, y;g_nCount = 0;for(x = 0; x < g_nWidth; x++)for(y = 0; y < g_nHeight; y++)if (getpixel(x, y) == WHITE)g_nCount++;// 计算目标数据g_pDst = new POINT[g_nCount];int i = 0;for(x = 0; x < g_nWidth; x++)for(y = 0; y < g_nHeight; y++)if (getpixel(x, y) == WHITE){g_pDst[i].x = x + (640 - g_nWidth) / 2;g_pDst[i].y = y + (480 - g_nHeight) / 2;i++;}// 恢复对屏幕的绘图操作SetWorkingImage(NULL);}// 获取源点集void GetSrcPoints(){// 设置随机种子srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));// 设置随机的源数据g_pSrc = new POINT[g_nCount];for(int i = 0; i < g_nCount; i++){g_pSrc[i].x = rand() % 640;g_pSrc[i].y = rand() % 480;}}// 全屏模糊处理(忽略屏幕第一行和最后一行)void Blur(DWORD* pMem){for(int i = 640; i < 640 * 479; i++){pMem[i] = RGB((GetRValue(pMem[i]) + GetRValue(pMem[i - 640]) + GetRValue(pMem[i - 1]) + GetRValue(pMem[i + 1]) + GetRValue(pMem[i + 640])) / 5,(GetGValue(pMem[i]) + GetGValue(pMem[i - 640]) + GetGValue(pMem[i - 1]) + GetGValue(pMem[i + 1]) + GetGValue(pMem[i + 640])) / 5,(GetBValue(pMem[i]) + GetBValue(pMem[i - 640]) + GetBValue(pMem[i - 1]) + GetBValue(pMem[i + 1]) + GetBValue(pMem[i + 640])) / 5);}}// 主函数void main(){// 初始化initgraph(640, 480);// 创建绘图窗口看DWORD* pBuf = GetImageBuffer();// 获取显示缓冲区指针GetDstPoints();// 获取目标点集GetSrcPoints();// 获取源点集// 运算int x, y;for (int i = 2; i <= 256; i += 2){COLORREF c = RGB(i - 1, i - 1, i - 1);Blur(pBuf);// 全屏模糊处理for (int d = 0; d < g_nCount; d++){x = g_pSrc[d].x + (g_pDst[d].x - g_pSrc[d].x) * i / 256;y = g_pSrc[d].y + (g_pDst[d].y - g_pSrc[d].y) * i / 256;pBuf[y * 640 + x] = c;// 直接操作显示缓冲区画点}Sleep(5);// 延时}// 清理内存delete g_pDst;delete g_pSrc;// 按任意键退出_getch();closegraph();} |
C语言网提供由在职研发工程师或ACM蓝桥杯竞赛优秀选手录制的视频教程,并配有习题和答疑,点击了解:
一点编程也不会写的:零基础C语言学练课程
解决困扰你多年的C语言疑难杂症特性的C语言进阶课程
从零到写出一个爬虫的Python编程课程
只会语法写不出代码?手把手带你写100个编程真题的编程百练课程
信息学奥赛或C++选手的 必学C++课程
蓝桥杯ACM、信息学奥赛的必学课程:算法竞赛课入门课程
手把手讲解近五年真题的蓝桥杯辅导课程